Subject & Paper: GS-3 (Science & Tech; Health), Prelims
What happened & why it matters.
India has licensed domestic companies to produce its first indigenous multi-stage malaria vaccine, developed by national research partners. “Multi-stage” means one vaccine mixes targets from different steps of the parasite’s life, aiming to block infection, blunt illness, and cut transmission—a three-way win that complements nets and medicines.
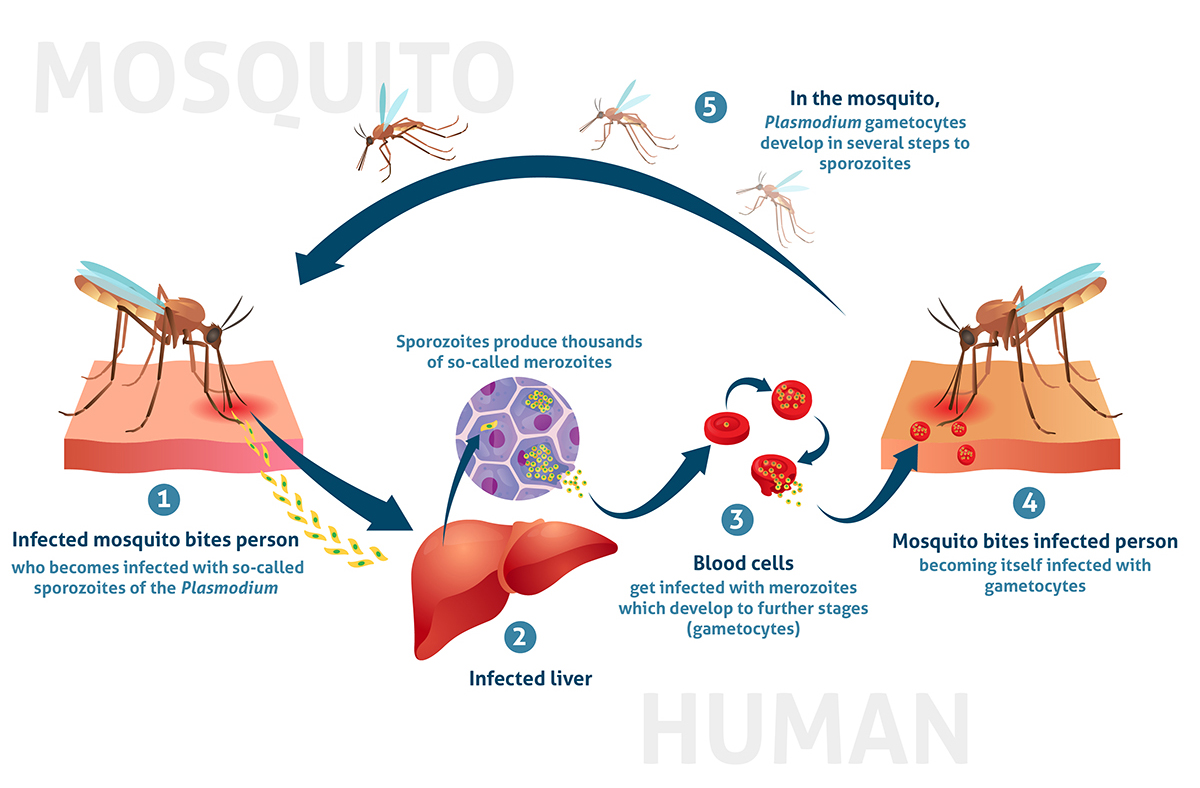
Malaria Life Cycle
- A mosquito bites and injects sporozoites (the “seed” form) → liver.
- In the liver, parasites multiply silently (no symptoms).
- They spill into blood as merozoites, invade red blood cells → fever, chills, anaemia.
- Some turn into gametocytes; when another mosquito bites, it picks them up.
- In the mosquito, parasites mature and get ready to infect the next person.
- Two major species in India: P. falciparum (severe) and P. vivax (relapse risk).
What “multi-stage” really does?
- Try to stop the infection early so fewer parasites ever reach the blood.
- Blood-stage targets: aim to reduce multiplication in RBCs, lowering fever severity and complications.
- Transmission-blocking targets: make antibodies that disable gametocytes in the mosquito gut, breaking the chain.
Think of it as multiple locks on multiple doors—even if one is picked, others slow or stop the intruder.
How India can roll it out
-
Start with the worst-hit districts first. Combine the vaccine with universal mosquito nets, rapid malaria tests, and effective treatment.
-
Keep cold storage ready for vaccines, and monitor carefully for any side effects, as is done with other vaccines.
-
Track the data closely: check which malaria species are spreading (falciparum or vivax), see if strains are changing, and note how long the vaccine protection lasts. Adjust booster doses as needed.
-
Community awareness: Explain clearly that the vaccine is an addition to nets and quick treatment, not a replacement.
Glossary.
- Efficacy vs effectiveness: Efficacy = trial performance; effectiveness = real-world impact.
- Antigen: A piece of the parasite that trains the immune system to recognise and attack.
- Vector control: Curtains, insecticide-treated bed nets, indoor spraying, larval source management.
What to remember for Prelims.
- “Multi-stage” = targets two or more parasite stages.
- Goals: prevent entry, reduce illness, block spread—together.
- Works with, not instead of, nets/ACTs/surveillance.
Prelims Question
Which statement best describes a multi-stage malaria vaccine?
A) Targets only the mosquito
B) Targets multiple parasite stages (e.g., liver and blood) to prevent infection and disease
C) Replaces bed nets
D) Cures those already sick without medicines
Answer: B.
One-line wrap.
Block entry, blunt illness, break transmission—one vaccine, many roadblocks for malaria.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Start Yours at Ajmal IAS – with Mentorship StrategyDisciplineClarityResults that Drives Success
Your dream deserves this moment — begin it here.


