Syllabus: GS-II & V- India and its neighbours
Why in the News?
Recent high-level exchanges between Assam and Bhutan—including Bhutan’s King visiting Assam in April 2024 and the Assam Chief Minister’s visit to Bhutan—have highlighted Assam’s expanding role in strengthening Indo-Bhutan relations under India’s Neighbourhood First Policy.
Assam’s Strategic Role in Indo-Bhutan Relations
Assam shares a 267-km border with Bhutan, touching the districts of Udalguri, Tamulpur, Baksa, Chirang, and Kokrajhar. This border geography makes Assam a pivotal gateway for Bhutan’s connectivity, trade, and security cooperation with India.
Key Reasons for Assam’s Importance
- It is a major transit corridor for Bhutanese goods and people.
- It acts as a buffer and security frontier in India’s Northeast.
- It enables cross-border ecological conservation, especially in the Manas landscape.
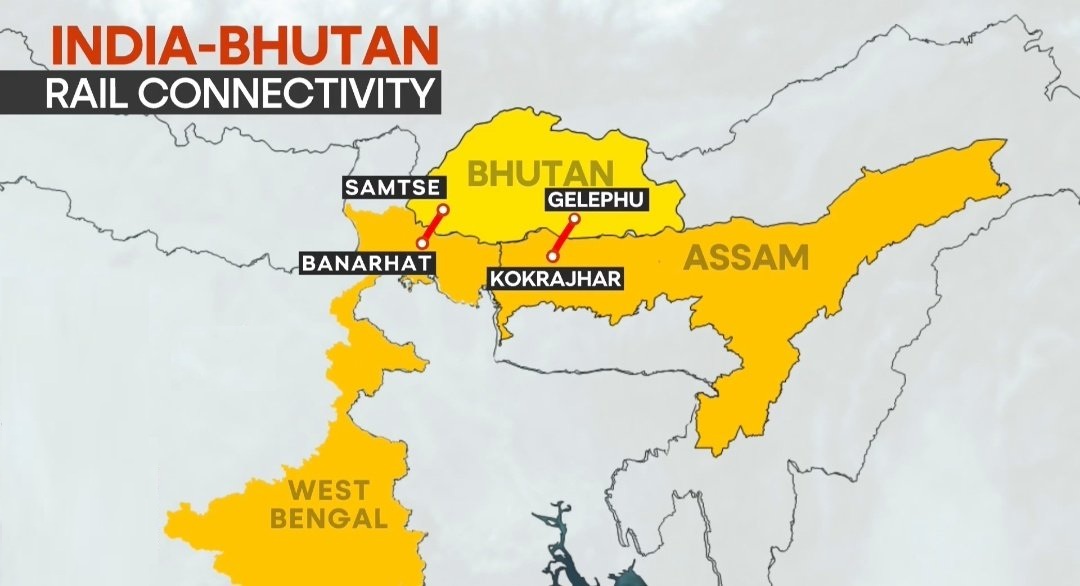
- It is becoming central to emerging connectivity projects such as the Jogighopa Multi-Modal Logistics Park & Kokrajhar–Gelephu (69 km, Assam–Bhutan).
Historical Foundations of India-Bhutan Ties
1. The 1949 Indo-Bhutan Treaty
Created the basis of the “special relationship,” giving India strategic responsibility while ensuring Bhutan’s autonomy.
2. The 2007 Revised Treaty
- Granted Bhutan the freedom to conduct independent foreign policy and procure arms
- Condition: actions must not jeopardise India’s national security
- Strengthened bilateral trust and institutional cooperation
3. Operation All Clear (2003)
- A critical moment where Bhutan, with India’s support, eliminated Assam-based insurgent groups (ULFA, NDFB, KLO) operating from Bhutanese soil.
- This operation permanently altered the security dynamic, establishing deep defence cooperation.
Strategic Significance for India
1. Security Dimensions
- Assam provides a frontline position to prevent hostile external influence in the eastern Himalayan region.
- Post-2017 Doklam standoff, Bhutan’s support to India reaffirmed the strategic closeness.
- Assam’s major bridges—Bogibeel, Dhola-Sadiya—strengthen rapid military mobility in crisis scenarios.
2. The Siliguri Corridor Factor
- Assam’s stability is essential to protect the narrow Chicken’s Neck, the lifeline connecting mainland India to the Northeast.
Assam as an Emerging Hub of Paradiplomacy
Paradiplomacy refers to sub-national governments engaging in international cooperation.
Assam is increasingly:
- Hosting Bhutanese delegations
- Participating in bilateral dialogues
- Facilitating cross-border infrastructure and trade
This represents a major shift in India’s diplomacy, where states complement central efforts.
Cross-Border Ecological Cooperation: The Manas Landscape
- Assam and Bhutan share one of South Asia’s richest biodiversity zones.
Transboundary Manas Conservation Area (TraMCA), 2011
A flagship ecological partnership involving:
- Joint patrolling
- Anti-poaching intelligence sharing
- Habitat monitoring
- Community-based conservation
Result: Tiger population more than doubled between 2010 and 2018, earning global conservation recognition in 2020.
New Connectivity Push: Linking People, Trade, and Economies
Jogighopa Multi-Modal Logistics Park (MMLP)
- Assam’s biggest logistics hub
- Enhances trade with Bhutan
- Supports Bhutan’s ambitious Gelephu Mindfulness City vision
- Integrates road, rail, and waterways for seamless cargo movement
Reopening of Border Gates
- Important gates reopened include: Darranga, Dadgiri, Gelephu, Namlang, Panbang, Samrang, strengthening people-to-people ties.
Commercial & Geopolitical Potential
The Indo-Bhutan border in Assam is transitioning from a traditionally peaceful frontier to a zone of:
- Trade expansion
- Tourism
- Energy partnerships
- Regional connectivity under the Act East Policy
Assam, positioned as a gateway to Bhutan and Southeast Asia, holds immense strategic weight.
Conclusion
Assam is no longer just a bordering state—it is emerging as a diplomatic, ecological, economic, and strategic bridge between India and Bhutan. Through connectivity projects, ecological partnerships, and paradiplomatic engagement, Assam is shaping a stronger bilateral relationship that supports India’s broader regional and geopolitical vision.
Exam Hook – Key Takeaways
- 267-km Indo-Bhutan border through five Assam districts
- Special relationship under 1949 Treaty, revised in 2007
- Operation All Clear crucial for Northeast security
- TraMCA showcased successful cross-border conservation
- MMLP at Jogighopa to boost trade and connectivity
- Assam central to Neighbourhood First & Act East

Mains Question
Assess the role of Assam in strengthening Indo-Bhutan relations. How do geography, security, ecology, and connectivity together shape this bilateral partnership? (250 words)
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Start Yours at Ajmal IAS – with Mentorship StrategyDisciplineClarityResults that Drives Success
Your dream deserves this moment — begin it here.